How long can sperm survive? All you need to know
When you’re trying to get pregnant, the timing of intercourse is crucial. A common question is how long sperm can survive inside the female body after ejaculation — and what affects their lifespan. Understanding this is important for optimizing the timing of intercourse and increasing the chances of conception. In this text, we explain how it works!
How Long Can Sperm Survive?
Sperm can survive much longer than many people think. Under optimal conditions, sperm can remain viable for up to five days after intercourse, although most survive for 2–3 days.
Several factors influence how long sperm can survive:
-
The quality of the cervical mucus
-
Sperm quality
-
The pH level of the vagina and cervix
-
Where the woman is in her menstrual cycle at the time of ejaculation
Fertility specialists generally consider a survival range of 3–5 days to be realistic.
Why Do Sperm Survive for Different Lengths of Time?
The woman’s intimate environment changes significantly throughout the menstrual cycle, directly affecting the sperm’s ability to survive and move forward. Learn more about your cycle here.
Survival During the Fertile Window
As you approach ovulation, cervical mucus becomes thinner and more permeable, richer in nutrients, and less acidic. In other words, it becomes more “sperm-friendly.”
Cervical mucus provides an ideal environment where sperm can survive longer and move more effectively toward the egg.
Survival Outside the Fertile Window
During the rest of the cycle, cervical mucus is thicker and stickier, less nutrient-rich, and more acidic – making it more difficult for sperm to penetrate.
Outside the fertile window of your cycle, sperm survive for a much shorter time, often only a few hours.
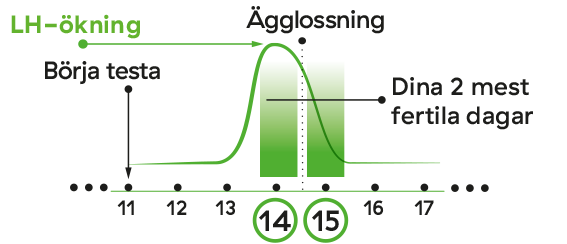
The Fertile Window and Ovulation
Your fertile window is the period during which you can become pregnant, and it lasts longer than just the day of ovulation — thanks to the sperm’s ability to survive for several days.
How long is the fertile window?
The fertile window usually includes the five days before ovulation, the day of ovulation itself, and one day after ovulation. This gives a total of about 6–7 days per cycle during which fertilization is possible.
Why is it important to have intercourse several times during the fertile window?
The egg can only be fertilized within 12–24 hours after ovulation. This short time frame means it’s important that sperm are already present when ovulation occurs, or that intercourse happens very soon afterward.
Optimal timing for intercourse is 2–3 days before the expected ovulation, the day before ovulation, and on the day of ovulation.
Having intercourse every other day throughout the fertile window can also make the process feel more relaxed, since it removes the pressure of trying to pinpoint the exact right day — something many people prefer.
Signs of Your Fertile Window
Recognizing when you are in your fertile window is key to maximizing your chances of getting pregnant. Here are some signs to look out for:
Changes in cervical mucus (discharge)
- Before the fertile phase, the discharge is thick and sticky, or there may be almost none at all.
- At the beginning of the fertile phase, the discharge becomes cream-like in consistency.
- At the peak of the fertile window, it becomes clear and stretchy, similar to raw egg white.
- After ovulation, the discharge quickly returns to a thicker consistency.
Body temperature
A slight temperature increase of 0.2–0.5°C occurs after ovulation. The temperature remains elevated until your next period. By measuring each morning, you can identify patterns in your cycle.
Physical symptoms
Some people experience mild pain on one side of the lower abdomen, slight spotting, and an increase in sex drive.
What affects how long sperm can survive?
Not all sperm have the same chance of survival. Several factors influence how long sperm can live inside the female reproductive system — some are genetic, while others are lifestyle-related.
Sperm quality
- Well-shaped and motile sperm tend to survive longer.
- Higher concentration increases survival chances, and healthy sperm navigate more effectively through cervical mucus.
Lifestyle factors
- Smoking and alcohol significantly reduce sperm quality.
- Stress can affect both sperm quality and quantity.
- Diet plays a role — antioxidants improve sperm health.
- Overheating, for example from frequent sauna visits or hot baths, can damage sperm.
Male age
- Sperm quality gradually decreases after age 35.
- Older men may have sperm with lower survival capacity, and DNA fragmentation increases with age.
Sexually transmitted infections
Infections such as chlamydia and gonorrhea can negatively affect sperm quality and in some cases reduce sperm survival. If you or your partner suspect an STI, or haven’t been tested in a long time, it may be wise to get tested — especially when trying to conceive.
Using an ovulation calendar and tests
To understand when you are ovulating and increase your chances of conceiving, we recommend using an ovulation calendar together with ovulation tests.
When to seek help to get pregnant
If pregnancy does not occur despite regular attempts, it is recommended to seek medical advice after one year of trying. If the woman is over 35, has irregular cycles, or has conditions such as PCOS or endometriosis, seeking help after six months may be appropriate. Men with known risk factors — for example reduced sperm function after chemotherapy — may also need an earlier evaluation.
Source: www.1177.se and fact-checked by RFSU clinic.